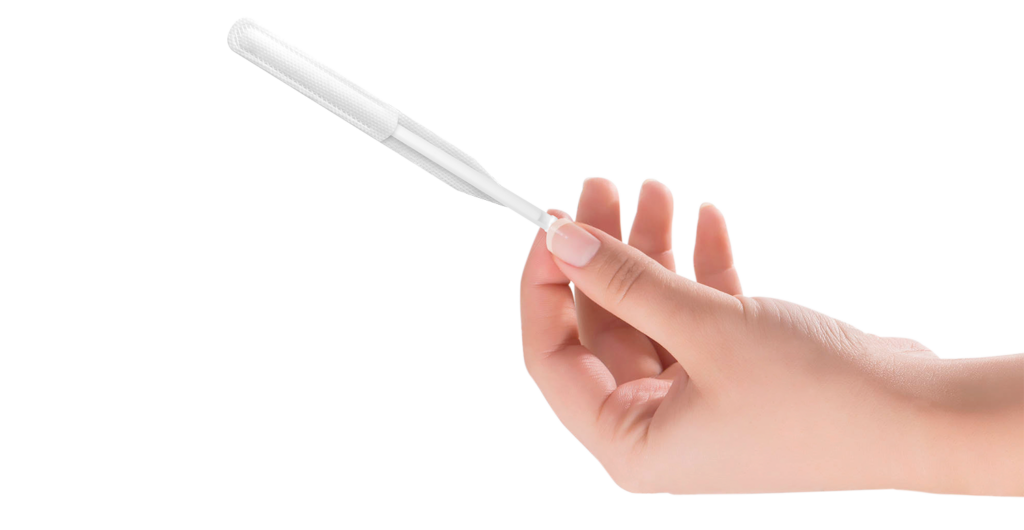
Cervical cancer (HPV)
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) are human papillomaviruses that can cause cervical cancer. HPV infection is a frequent occurrence, with 80% of women having an HPV infection in their lifetime. In most cases, this infection is eliminated naturally.
In 10% of cases, it can persist and lead to abnormalities (precancerous lesions) on the cervix. These lesions may disappear naturally or persist, with possible progression over the years to cervical cancer.
In France, the screening test is recommended for those aged 25 and over, and is performed by two cytological examinations (cervical smears) one year apart. If the results are normal, the next screening test takes place 3 years later, with a new smear or HPV test, depending on age. If the result of this test is abnormal, HPV can be detected.
After age 30, HPV testing by PCR is recommended. A smear test is necessary if the virus is detected.
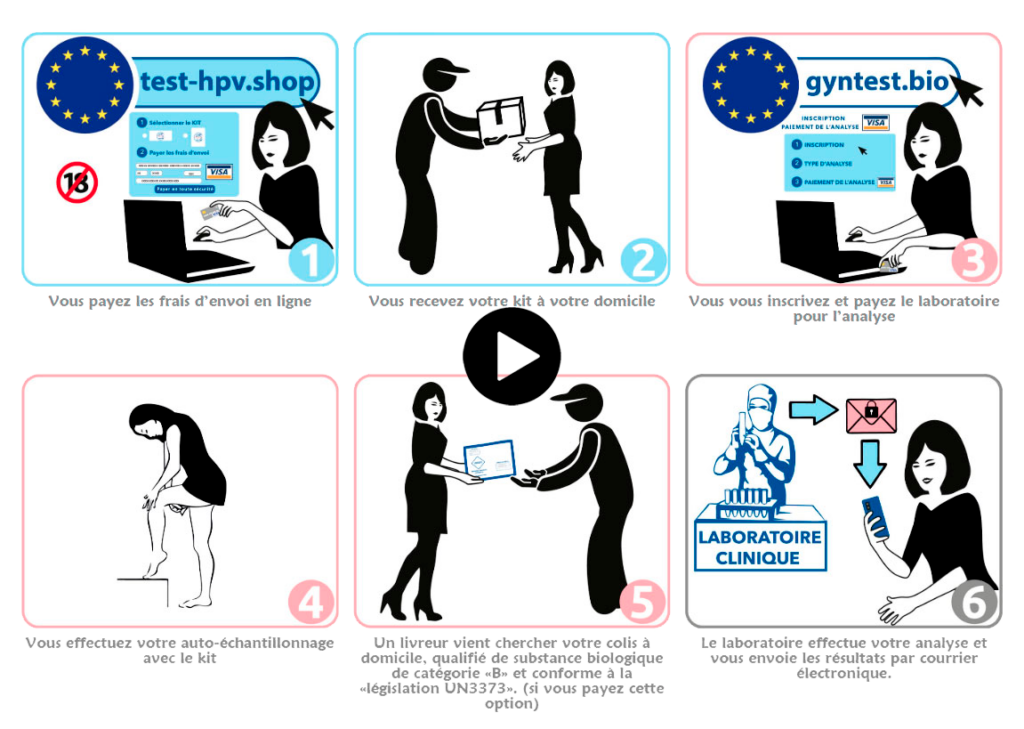
Self-sampling is analyzed in a COFRAC-accredited French medical biology laboratory, which delivers reliable results validated by a medical biologist.