Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Chlamydia trachomatis is a bacterium primarily responsible for genital chlamydia. Although this sexually transmitted infection (STI) can manifest as genital infections, primarily in women, many individuals carry the bacteria without knowing it. However, if detected early, the infection can be easily treated with antibiotics
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (or gonococcus) is a highly contagious bacterium responsible for gonorrhea, blennorrhea, and gonococcal infections. In women, gonococcal infections are typically asymptomatic or may not produce recognizable symptoms until complications arise.
- Genital mycoplasmas are small bacteria widely distributed in nature. In the case of Mycoplasma genitalium, its presence is considered pathogenic. In women, the presence of Mycoplasma genitalium is associated with various pathologies of the female genital tract, such as cervicitis, urethritis, and upper pelvic infection.
- Trichomonas vaginalis is a human parasite belonging to the protozoan family. It is responsible for a sexually transmitted infection that is most often mild. Trichomoniasis primarily manifests as vulvovaginitis accompanied by vaginal discharge, which is often abundant, foul-smelling or not, with a frothy appearance, sometimes taking on a greenish or whitish color.

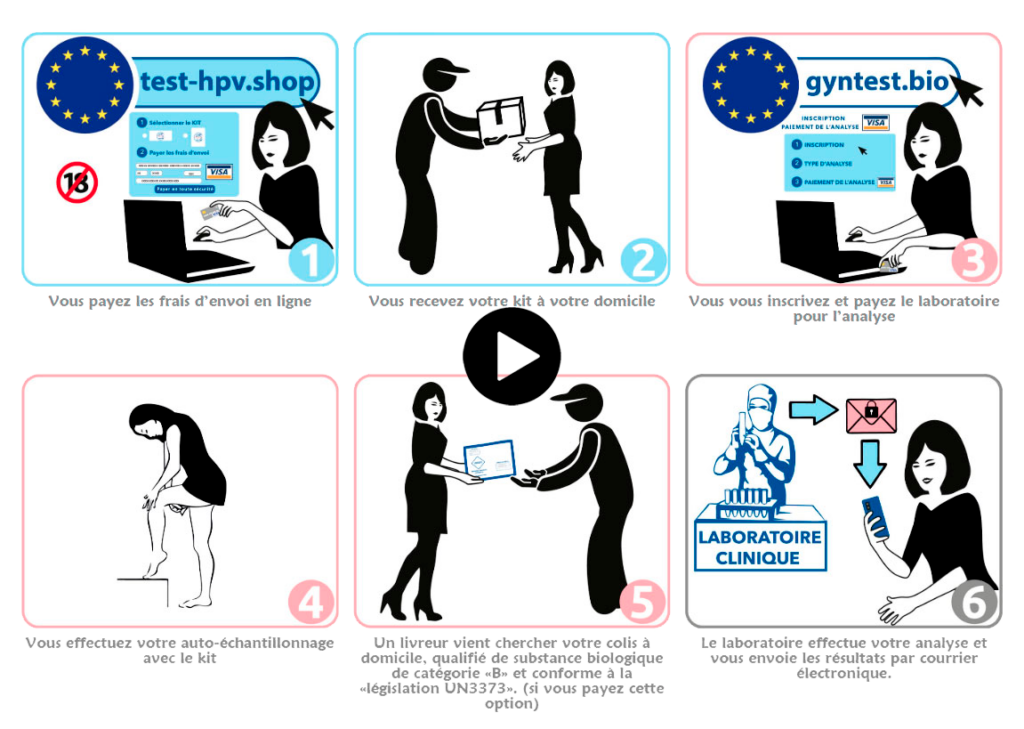
Self-sampling is analyzed in a COFRAC-accredited French medical biology laboratory, which delivers reliable results validated by a medical biologist.